
This edition of the 𝘼𝙜𝙞𝙡𝙚 𝙄𝙣𝙣𝙤𝙫𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙣𝙜 ™ Newsletter is for Innovators, Entrepreneurs, and Business Leaders who want faster, more reliable, innovating outcomes.
Innovating can seem like a complicated and complex endeavor made even more difficult by the uncertainty of outcomes and the consequent risk of project failure. By clearly identifying what you are trying to accomplish and why, and scope of change you are seeking to make, projects become much simpler and faster with more reliable outcomes.
In this edition of the newsletter, we outline the more common types of innovation projects and provide some guidance for how to align the project effort with the outcomes you are targeting using a Job-To-Be-Done framework.
A common heuristic used to classify innovation endeavors is a description distinguishing project types by success rate. The project classifications, and their typical success rates (i.e. projects achieving their performance targets and outcomes) are:
· Continuous Improvement Projects 70%
· Incremental Innovating Projects 55%
· Sustaining Innovating Projects 40%
· Radical Innovating Projects 15%
In general, as the complicated and complex nature of the project increases, the uncertainty of what to do and how to do it also increases, which is reflected in the declining project success rate.
Business Leaders have many choices of methodologies and approaches to grow the business. Lean Manufacturing, Lean Start-Up, 80/20 Principles, and Stage-Gate NPD are just a few examples. If you want to grow the business through New Solution Innovation, the Job-To-Be-Done Framework provides the most effective and reliable methodology and approach.
The JTBD (Job-To-Be-Done) framework evaluates what is currently being accomplished by an available solution, what improvement is possible, and why the progress towards a better outcome is desirable. The advantages of the JTBD framework are in the constraints imposed by focusing on the situation you are addressing, the trouble with the existing solution you are trying to mitigate or alleviate, and the focus on progress towards a better solution rather than an arbitrary goal that may or may not be achievable.
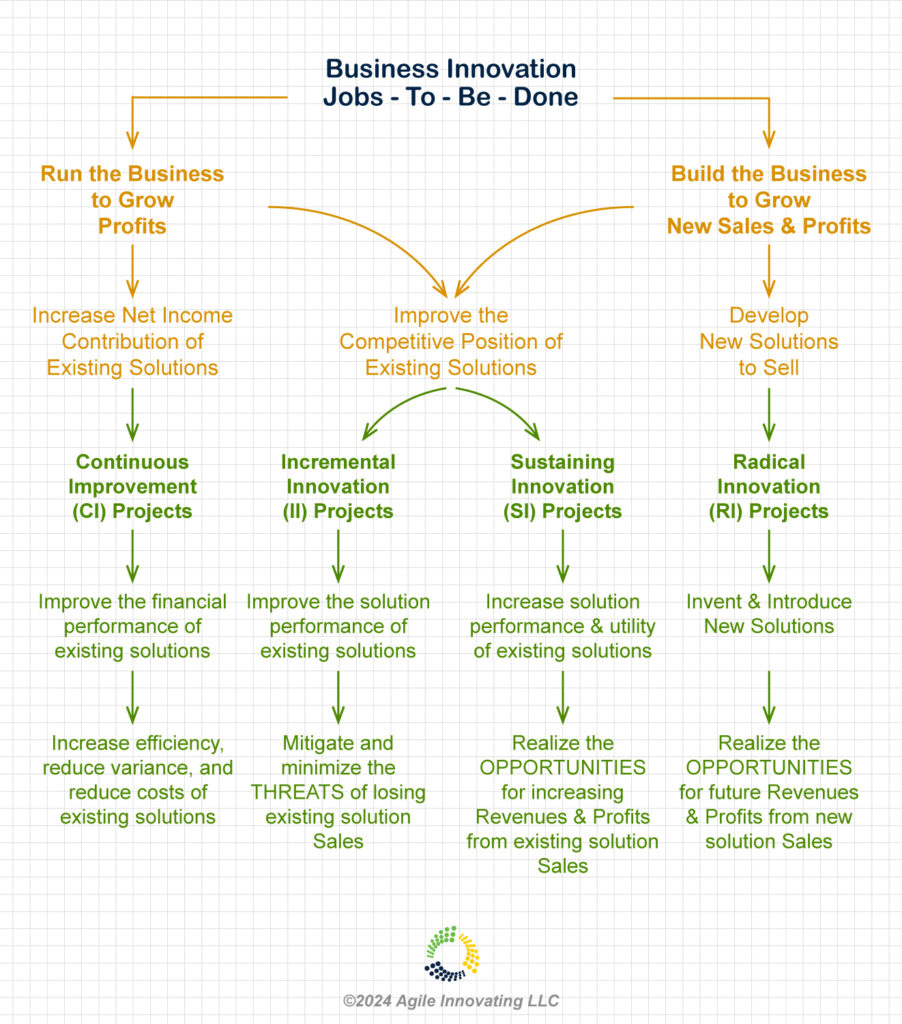
At the business Stakeholder level, there are two Jobs-To-Be-Done; “Run the Business” and “Build the Business”.
The progress you are trying to make in “Running the Business” is increasing the financial contribution of existing solutions to business goals.
Both “Running the Business” and “Building the Business” situations share the progress towards improving the competitive position of existing solutions for current customer segments to increase current Revenues and Profits.
The progress you are trying to make in “Building the Business” is creating new solutions to sell to existing and new customer segments that increase future Revenues and Profits.
Continuous Improvement (CI) Projects
The genesis of CI Projects is in the Stakeholder’s desire to “Run the Business” better and increase the financial contribution of existing solutions. CI Projects focus on increasing efficiency, reducing variance of outputs and outcomes, and reducing costs.
Incremental Innovating (II) Projects
The genesis of II Projects is in the Stakeholder’s desire to “Run the Business” better and improve the competitive position of existing solutions to deal with the competitive THREATS of losing current Sales. II Projects focus on improving the performance of existing solutions to improve the user experience within current customer segments.
Sustaining Innovating (SI) Projects
The genesis of SI Projects is in the Stakeholder’s desire to “Build the Business” by identifying and realizing OPPORTUNITIES for increasing Revenues and Profits from existing solutions. SI Projects focus on increasing the performance and utility of existing solutions to improve the user experience within current customer segments.
Radical Innovating (RI) Projects
The genesis of RI Projects is in the Stakeholder’s desire to “Build the Business” by identifying and realizing the OPPORTUNITIES for future Revenues and Profits from new Sales of new solutions. RI Projects focus on the Invention and Introduction of new solutions to existing and new customer segments providing better user experiences.
Conclusion
The JTBD framework helps to makes sense of the different kinds of innovating projects that you could engage in. By understanding what you’re trying to do and why, and the progress you want to make as an outcome of the project, your success rates within each class of project increases. Innovating, and the change you seek to make, become easier. With discipline and practice, Innovations as an outcome of Innovating Projects become the norm rather than the exception.
🌱
Purpose, what, and why
Progress towards a better life
A job to be done
-Innovation Haiku, Kevin A Fee, May 15, 2024
To learn more about the complete Agile Innovating, LLC systemic practice that accelerates business growth through innovation, please contact us at [email protected]
